Interaction tests
As you build more complex UIs like pages, components become responsible for more than just rendering the UI. They fetch data and manage state. Interaction tests allow you to verify these functional aspects of UIs.
In a nutshell, you start by supplying the appropriate props for the initial state of a component. Then simulate user behavior such as clicks and form entries. Finally, check whether the UI and component state update correctly.
In Storybook, this familiar workflow happens in your browser. That makes it easier to debug failures because you're running tests in the same environment as you develop components: the browser.
How does component testing in Storybook work?
You start by writing a story to set up the component's initial state. Then simulate user behavior using the play function. Finally, use the test-runner to confirm that the component renders correctly and that your interaction tests with the play function pass. Additionally, you can automate test execution via the command line or in your CI environment.
- The
playfunction is a small snippet of code that runs after a story finishes rendering. You can use this to test user workflows. - The test is written using Storybook-instrumented versions of Jest and Testing Library.
@storybook/addon-interactionsvisualizes the test in Storybook and provides a playback interface for convenient browser-based debugging.@storybook/test-runneris a standalone utility—powered by Jest and Playwright—that executes all of your interactions tests and catches broken stories.
Set up the interactions addon
To enable interaction testing with Storybook, you'll need to take additional steps to set it up properly. We recommend you go through the test runner documentation before proceeding with the rest of the required configuration.
Run the following command to install the interactions addon and related dependencies.
npm install @storybook/testing-library @storybook/jest @storybook/addon-interactions --save-devUpdate your Storybook configuration (in .storybook/main.js|ts) to include the interactions addon and enable playback controls for debugging.
module.exports = {
stories: ['../src/**/*.stories.mdx', '../src/**/*.stories.@(js|jsx|ts|tsx)'],
addons: [
// Other Storybook addons
'@storybook/addon-interactions', // 👈 Addon is registered here
],
features: {
interactionsDebugger: true, // 👈 Enable playback controls
},
};Write an interaction test
The test itself is defined inside a play function connected to a story. Here's an example of how to set up an interaction test with Storybook and the play function:
import React from 'react';
import { ComponentStory, ComponentMeta } from '@storybook/react';
import { within, userEvent } from '@storybook/testing-library';
import { expect } from '@storybook/jest';
import { LoginForm } from './LoginForm';
export default {
/* 👇 The title prop is optional.
* See https://storybook.js.org/docs/6/configure#configure-story-loading
* to learn how to generate automatic titles
*/
title: 'Form',
component: LoginForm,
} as ComponentMeta<typeof LoginForm>;
const Template: ComponentStory<typeof LoginForm> = (args) => <LoginForm {...args} />;
export const EmptyForm = Template.bind({});
/*
* See https://storybook.js.org/docs/6/writing-stories/play-function#working-with-the-canvas
* to learn more about using the canvasElement to query the DOM
*/
export const FilledForm = Template.bind({});
FilledForm.play = async ({ canvasElement }) => {
const canvas = within(canvasElement);
// 👇 Simulate interactions with the component
await userEvent.type(canvas.getByTestId('email'), 'email@provider.com');
await userEvent.type(canvas.getByTestId('password'), 'a-random-password');
// See https://storybook.js.org/docs/6/essentials/actions#automatically-matching-args to learn how to setup logging in the Actions panel
await userEvent.click(canvas.getByRole('button'));
// 👇 Assert DOM structure
await expect(
canvas.getByText(
'Everything is perfect. Your account is ready and we should probably get you started!'
)
).toBeInTheDocument();
};Once the story loads in the UI, it simulates the user's behavior and verifies the underlying logic.
API for user-events
Under the hood, Storybook’s interaction addon mirrors Testing Library’s user-events API. If you’re familiar with Testing Library, you should be at home in Storybook.
Below is an abridged API for user-event. For more, check out the official user-event docs.
| User events | Description |
|---|---|
clear | Selects the text inside inputs, or textareas and deletes it userEvent.clear(await within(canvasElement).getByRole('myinput')); |
click | Clicks the element, calling a click() function userEvent.click(await within(canvasElement).getByText('mycheckbox')); |
dblClick | Clicks the element twice userEvent.dblClick(await within(canvasElement).getByText('mycheckbox')); |
deselectOptions | Removes the selection from a specific option of a select element userEvent.deselectOptions(await within(canvasElement).getByRole('listbox','1')); |
hover | Hovers an element userEvent.hover(await within(canvasElement).getByTestId('example-test')); |
keyboard | Simulates the keyboard events userEvent.keyboard(‘foo’); |
selectOptions | Selects the specified option, or options of a select element userEvent.selectOptions(await within(canvasElement).getByRole('listbox'),['1','2']); |
type | Writes text inside inputs, or textareas userEvent.type(await within(canvasElement).getByRole('my-input'),'Some text'); |
unhover | Unhovers out of element userEvent.unhover(await within(canvasElement).getByLabelText(/Example/i)); |
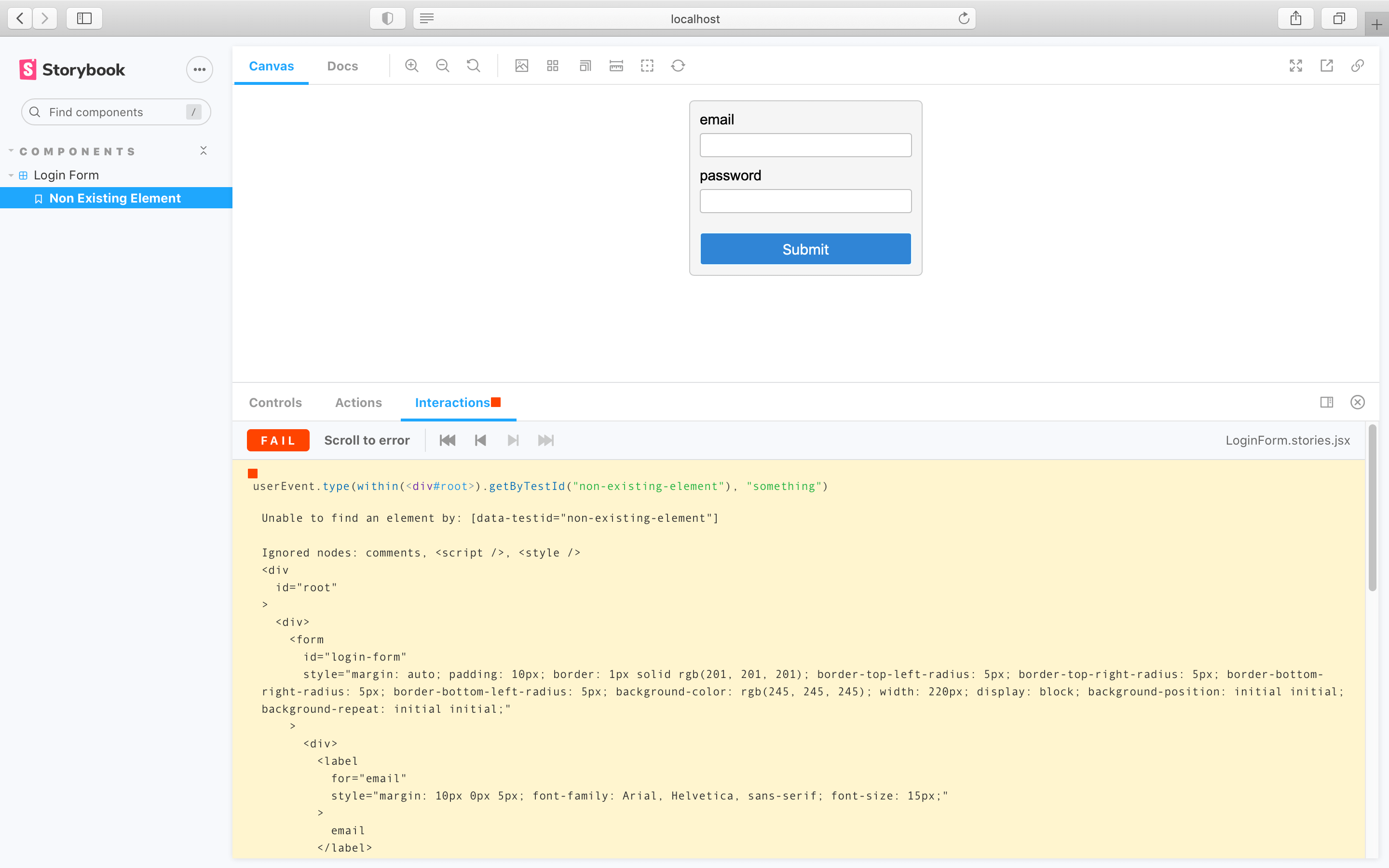
Interactive debugger
If you check your interactions panel, you'll see the step-by-step flow. It also offers a handy set of UI controls to pause, resume, rewind, and step through each interaction.
Permalinks for reproductions
The play function is executed after the story is rendered. If there’s an error, it’ll be shown in the interaction addon panel to help with debugging.
Since Storybook is a webapp, anyone with the URL can reproduce the error with the same detailed information without any additional environment configuration or tooling required.
Streamline interaction testing further by automatically publishing Storybook in pull requests. That gives teams a universal reference point to test and debug stories.
Execute tests with the test-runner
Storybook only runs the interaction test when you're viewing a story. Therefore, you'd have to go through each story to run all your checks. As your Storybook grows, it becomes unrealistic to review each change manually. Storybook test-runner automates the process by running all tests for you. To execute the test-runner, open a new terminal window and run the following command:
npm run test-storybook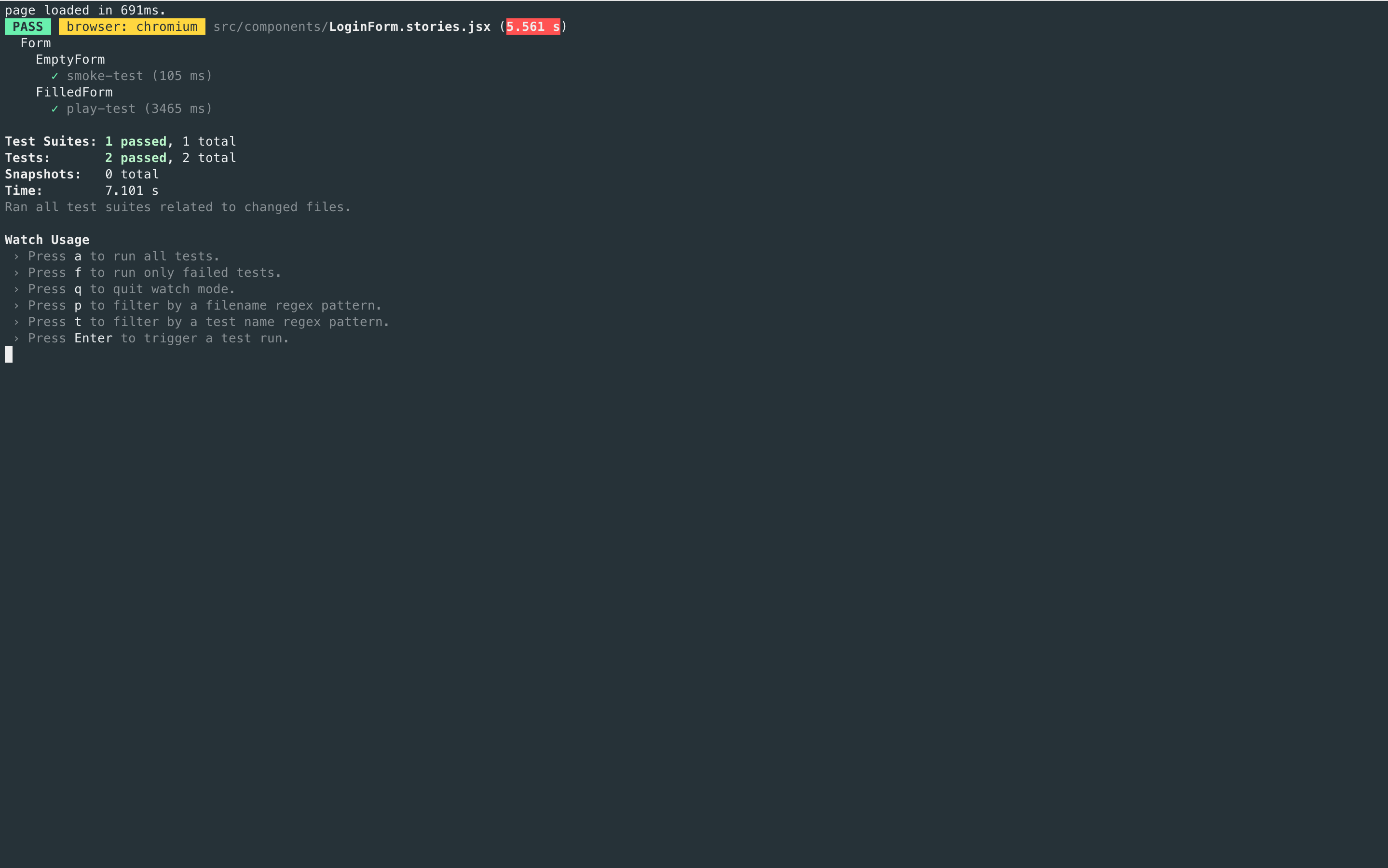
If you need, you can provide additional flags to the test-runner. Read the documentation to learn more.
Automate
Once you're ready to push your code into a pull request, you'll want to automatically run all your checks using a Continuous Integration (CI) service before merging it. Read our documentation for a detailed guide on setting up a CI environment to run tests.
What’s the difference between interaction tests and visual tests?
Interaction tests can be expensive to maintain when applied wholesale to every component. We recommend combining them with other methods like visual testing for comprehensive coverage with less maintenance work.
What's the difference between interaction tests and using Jest + Testing Library alone?
Interaction tests integrate Jest and Testing Library into Storybook. The biggest benefit is the ability to view the component you're testing in a real browser. That helps you debug visually, instead of getting a dump of the (fake) DOM in the command line or hitting the limitations of how JSDOM mocks browser functionality. It's also more convenient to keep stories and tests together in one file than having them spread across files.
Learn about other UI tests
- Test runner to automate test execution
- Visual tests for appearance
- Accessibility tests for accessibility
- Interaction tests for user behavior simulation
- Coverage tests for measuring code coverage
- Snapshot tests for rendering errors and warnings
- Import stories in other tests for other tools
